Risk management
Risk management framework
Enterprise risk management
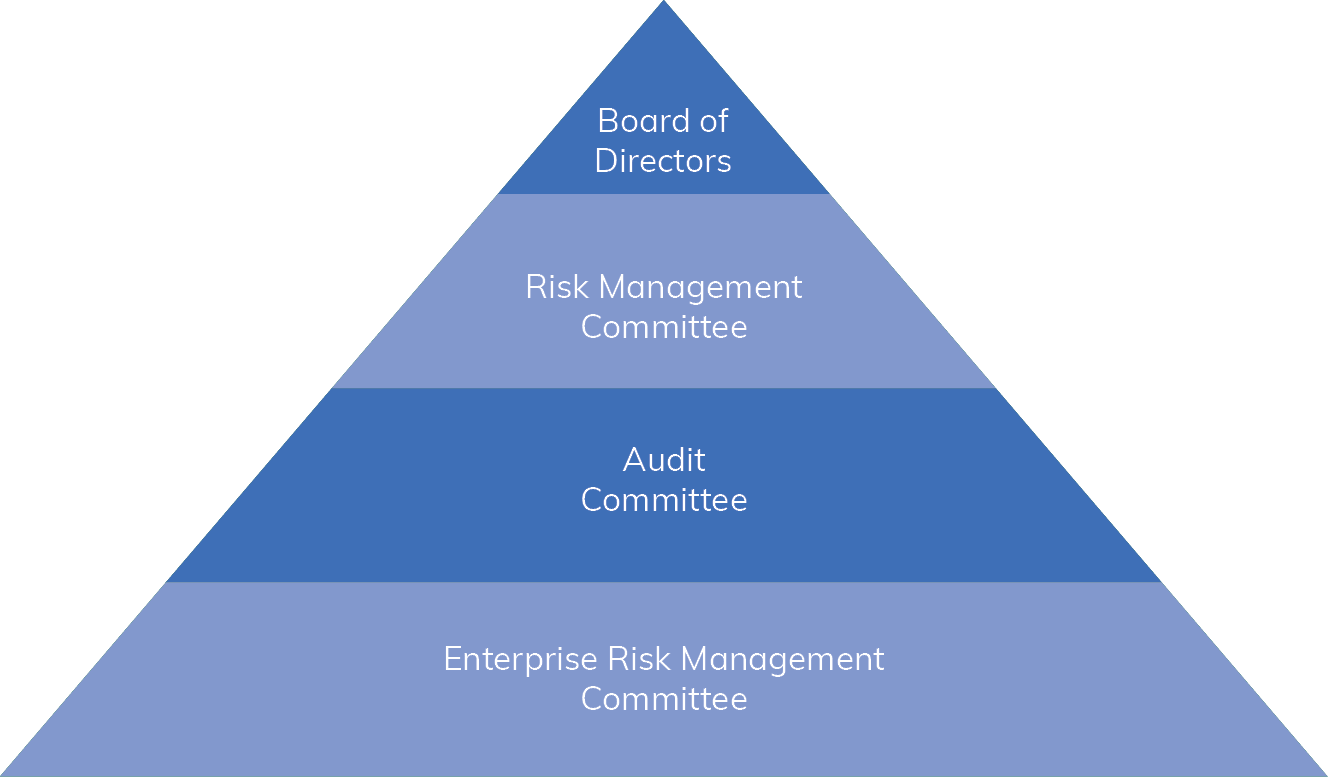
Enterprise risk management (ERM) of our Company involves identifying, evaluating, prioritising, categorising, mitigating, monitoring and reporting principal risks through bottom-up and top-down approaches. The bottom-up approach engages businesses and cross-functional teams in risk identification and mitigation planning, while the top-down approach ensures comprehensive framework effectiveness and long-term risk strategising. Risks are categorised into major themes to prioritise their mitigation strategies, overseen by an ERM council of Senior Management officials and the Risk Management Committee of the Board.

Risk identification
Aims at discovering crucial risks, mapping out the root causes or contributing factors.

Risk evaluation and prioritisation
Aims at defining risk priorities and ownership of essential risks, assessing differing impacts, considering risk appetite and existing mitigation measures.

Risk categorisation
Aims at understanding the diverse impact of risks and the degree of influence on their causes. It involves recognising various processes, identifying the root causes and gaining a clear understanding of risk associations.

Risk mitigation
Aims at addressing vital risks to limit their impact to a manageable level (within the stated risk appetite). It requires explicit action planning, assigning responsibilities and setting milestones.

Risk reporting and oversight
Aims at providing the Audit Committee and the Board with regular information on risk profile changes and mitigation strategies.
Risk mapping
We recognise that risks are inherent in any business, hence rather than avoiding them, we focus on identifying, monitoring and mitigating them. Effective risk management is essential for building resilience and ensuring sustainable growth. We regularly assess risks and take proactive measures to minimise their impacts. Key risks identified that may impact the business include:
Risk categories and descriptions
Approach to risk management:
Enterprise risk management (ERM) is a core component of the business model of our Company and the framework has progressively matured over the years. It encompasses the identification, classification, assessment, prioritisation, mitigation, monitoring and reporting of key risks.
We employ both bottom-up and top-down approaches to implement ERM effectively. The bottom-up approach involves the identification and regular assessment of risks by individual business units and cross-functional teams, along with the development of structured mitigation plans. A top-down approach complements this, with Senior Management ensuring the robustness of the framework, assessing the effectiveness of mitigation strategies and addressing long-term and macro-level risks.
To establish clear focus areas and prioritise mitigation efforts, risks are categorised under major themes. To oversee this process, our Company has established an ERM Council comprising members of Senior Management. The ERM is overseen by the Board of Directors through the Risk Management Committee of the Board.
| Key risk | Risk category | Risk description |
|---|---|---|
| Digitalisation risk | Strategic | Negative impacts or vulnerabilities that arise from adopting and relying on digital technologies |
| Geopolitical risk | Strategic | Negative impacts on business due to international political | key events (wars, trade disputes, elections, sanctions, etc) |
| Business performance risk | Operational | Inability to achieve business targets due to external and internal performance-related factors |
| Cyber risk | Operational | Data loss and business disruptions caused by cyberattacks |
| Supply chain risk | Operational | Disruptions in obtaining necessary resources and delivering goods or services |
| Talent risk | Operational | Challenges of attracting and retaining key talent |
| Adverse regulatory risk | Regulatory | Impacts on business arising from changes in laws, regulations or government policies |
| Compliance risk | Regulatory | Damages from failing to adhere to industry standards, laws and regulations |
| Sustainability risk | Sustainability | Failure to address the climate change-related risks, by not prioritising efforts towards lowering carbon emissions, advancing circular economy initiatives (related to water, waste and renewable resources) and conserving nature and biodiversity |
| Safety risk | Reputation | Deficiency in containment of safety hazards (process, product and workplace) |
Capitals
-

Financial
-

Manufactured
-

Human
-

Natural
-

Intellectual
-

Social and relationship
Risk category: Strategic
Digitalisation risk
Negative impacts or vulnerabilities that arise from adopting and relying on digital technologies
Capital linkages
Oversight
- Risk Management Committee
- IT Security Council*
Mitigation plans
- Enhance technology infrastructure
- Improve data maturity
- Prepare a long-term digital strategy with periodic reviews
Opportunities
- Achieve cost optimisation and process efficiency
- Leverage artificial intelligence, internet of things, cloud computing and machine learning to enhance efficiency, automate workflows and support real-time data-driven decision-making
Geo-political risk
Negative impacts on business due to international political | key events (wars, trade disputes, elections, sanctions, etc)
Capital linkages
Oversight
- Audit Committee
- Risk Management Committee
- Senior Management*
Mitigation plans
- Establish volume and price contracts with customers and ensure consistent service levels are maintained
- Monitor import volumes and prices and adjust the sales strategy accordingly
- Track macro-economic indicators and industry forecasts, while maintaining a strong focus on both variable and fixed costs across all entities
Opportunities
- Drive input cost reduction initiatives
- Maximise customer engagement through targeted strategies
Risk category: Operational
Business performance risk
Inability to achieve business targets due to external and internal performance-related factors
Capital linkages
Oversight
- Risk Management Committee
- Senior Management*
Mitigation plans
- Establish long-term agreements with customers
- Focus on new customers, geographies and products
- Take necessary and timely trade remedy measures to counter dumping from China
Opportunities
- Drive innovation to overcome external and internal challenges
- Improve efficiency and productivity and make the business future-ready
*Management Committee
Cyber risk
Data loss and business disruptions caused by cyberattacks
Capital linkages
Oversight
- Risk Management Committee
- IT Security Council*
Mitigation plans
- Conduct periodic vulnerability assessments and penetration testing for critical assets and applications
- Enhance governance over data security and access controls
- Provide regular security awareness training
Opportunities
- Enhance trust and reputation among all stakeholders
- Reduce instances of business disruption
Supply chain risk
Disruptions in obtaining necessary resources and delivering goods or services
Capital linkages
Oversight
- Audit Committee
- Risk Management Committee
Mitigation plans
- Develop alternate sources to reduce single source risks
- Enter into long-term contracts with transporters and forwarding agents
- Source alternate materials to reduce dependency
Opportunities
- Boost customer satisfaction by ensuring continuity and reliability of supply chain
- Enhance supply chain resilience by diversifying sourcing and building agile networks to better withstand disruptions, and meet sustainability and efficiency goals
Talent risk
Challenges of attracting and retaining key talent
Capital linkages
Oversight
- Nomination and Remuneration Committee
- Risk Management Committee
Mitigation plans
- Accelerate career progression for high-potential team members
- Enrich skills through trainings and job rotations
- Explore avenues for cross-functional deputations and growth through internal job postings
Opportunities
- Develop future-ready competencies
- Provide avenues for career growth
*Management Committee
Risk category: Regulatory
Adverse regulatory risk
Impacts on a business arising from changes in laws, regulations or government policies
Capital linkages
Oversight
- Audit Committee
- Risk Management Committee
Mitigation plans
- Collaborate with industry bodies, particularly those that convey industry perspectives to government departments involved in policy formulation and the issuance of regulations and notifications
- Engage in ongoing dialogues, meetings and conversations with regulatory authorities
- Monitor draft notifications and proposals from both the government and industry bodies, as well as identify potential risks that may arise
Opportunities
- Plan and strategise to ensure adherence to timelines and regulatory compliances
- Transition proactively to more sustainable regimes
Compliance risk
Damages from failing to adhere to industry standards, laws and regulations
Capital linkages
Oversight
- Audit Committee
- Risk Management Committee
Mitigation plans
- Conduct periodic compliance training
- Ensure timely updates and enforcement of policies and legal statues
- Monitor the whistleblower reporting system regularly
Opportunities
- Build a reputation as an ethical and trustworthy organisation
- Foster a culture of continuous learning to minimise incidents
*Management Committee
Risk category: Sustainability
Sustainability risk
Failure to address the climate change-related risks by not prioritising efforts towards lowering carbon emissions, advancing circular economy initiatives (related to water, waste and renewable resources) and conserving nature and biodiversity
Capital linkages
Oversight
- Risk Management Committee
- ESG Committee *
Mitigation plans
- Align sustainability goals with leadership KPIs and monitor risks against the sustainability targets of all businesses and functions
- Collaborate with supply chain partners to reduce the carbon footprint of the entire value chain
- Work closely with key customers to reduce carbon intensity of selected products
Opportunities
- Build a strong customer franchise for sustainable products
- Drive business growth that is profitable and sustainable
Risk category: Reputation
Safety risk
Deficiency in containment of safety hazards (process, product and workplace)
Capital linkages
Oversight
- Risk Management Committee
- EHS Committee*
Mitigation plans
- Automate processes | upgrade technologies
- Conduct safety audits regularly
- Implement a safety program to address cultural changes, employee behaviour, physical workplace standards and process safety management.
Opportunities
- Drive process automation
- Enhance the standards at workplace
*Management Committee